Identifying pupils with MLD
Assessment affects who is identified as having MLD and is relevant to pupils, their parents and teachers. This unit will introduce and illustrate some of the assessment and identification issues in practice.
You will learn about:
- Assessment and identification issues in MLD.
- Key factors to consider when identifying MLD.
- The different purposes of assessment.
- The process for conducting teaching assessment.
According to the Government’s working definition of MLD...
Significantly lower attainment
Needs not met by the curriculum
Pupils must be receiving additional educational provision
Greater difficulties than peers
Other associated issues
Task 1: design of teaching assessment
- 1.1 Identifying two pupils
- 1.2 Preparing questions
- 1.3 Preparation and implementation
- Close
- 1.3.1 Preparation
- 1.3.2 Suggested teaching approaches
- 1.3.3 Assessment process
It is vital that you’re properly prepared for the teaching in phases 1 and 2 if the assessment is going to be as successful and effective as possible:
- You should have planned approaches and options ready to use, but these should be flexible, allowing you to incorporate new approaches that emerge while teaching.
- The teaching assessment could be for a period of 10-15 minutes.
- You can return to the teaching the next day and try again, perhaps to check the consistency of pupils’ responses to the teaching.
When working through phases 1 and 2, be mindful of incorporating these elements into your approach:
- Explaining the context and task to the pupil, with the aim of helping them solve the problem.
- Using questions and prompts, for example going over how the child has solved similar problems in the past.
- Encouraging and supporting the pupil as they work through the problem; focusing on the effort of solving it, rather than rushing to an answer.
- Using tangible objects such as models, and visual references like number lines and alphabets, to help the child work through the problem.
- Doing the initial groundwork with the child and gradually introducing prompts to help them reach a solution, but only when required.
- Using analysis to break the task into sub-tasks, and presenting these in a sequential order, from introducing the problem to solving it.
After completing your preparation, you should be ready to carry out the teaching assessment. This is the process you should follow:
- Initially just present questions 1 and 3 to the pupils in written and verbal formats. This is a pre-teaching assessment; at this stage, simply explain what they will be doing and that you will help later on.
- Now you should focus the pupils’ teaching on question 2. Once you have completed teaching them how to solve this problem, and the process that goes into this, you can return to the other questions to observe their performance change.
- Return to questions 1 and 3. Work through these with the pupils and assess how their learning performance for these types of questions has changed as a result of being taught question 2.
- 1.4 Recording responses to teaching assessment
- 1.5 Recording teaching approaches used
- 1.6 Evaluating your findings
First, you will need to choose two pupils to assess: one identified as having MLD as their main area of SEN in the School Census, and one of the same gender and a similar age with below average attainment.
For the child with MLD:
- Ideally choose a pupil you teach or have previously taught.
- Discuss the model and criteria that were used to identify the pupil as having MLD with your school’s SENCO.
- Find out about other areas relevant to the definition from files and discuss with other teachers.
- Talk to the pupil on a one-to-one basis about learning approaches etc.
For the pupil with low attainment:
- Select a pupil with well below average attainment in maths, English and science, but not to the point where SEN or MLD have been considered as relevant categories.
Phase 1 focuses on verbal analogy problems, and phase 2 on series problems. You must complete phase 1 in its entirety before beginning phase 2.
You will need to set three kinds of questions for both phases, designed to monitor how successful the teaching is for the pupil’s learning. These should be the same for both pupils:
- Question 1 should be at ‘just cannot do’ level; that is to say, the pupil will not be able to comprehensively consider and answer the question without the teaching carried out for question 2.
- Question 2 should be a different version of question 1, at the same level of difficulty. This is for teaching purposes only.
- Question 3 is then designed to be a transfer task; it should be related to, but different from, question 1. For example, in phase 1, this can mean switching from word analogies based on opposites to relating an activity to a venue. For a series problem, you can switch from numbers to letters. See Appendix 1 of your PDF for more help on designing questions; word analogy and series problem examples also follow within these digital resources.
At this point, you’ll need to record the two pupils’ responses to reach conclusions for your assessment.
You can use a copy of Table 3 in your PDF to do this. Thinking of both phase 1 (word analogies) and phase 2 (series problems), note down whether the teaching led to performance changes from pre- to post-teaching for questions 1 and 3.
Compare the difference of any such changes between the two pupils.
Use a copy of Table 4 in your PDF to record the teaching approaches you employed during the process. Think about the techniques you used to promote enhanced performance on the questions in both phases. Referring to more extensive notes made during the process should help you pick out the salient points.
Use Table 8.5 to record and summarise what you learned from the teaching assessment. Think about this in the context of your initial objectives:
- Establishing the appropriateness of the identification for both pupils.
- Seeing how the pupils respond to teaching, bearing in mind their respective identifications, and what kinds of teaching might help them improve their learning.
A list of questions to ask yourself post-teaching can be found in your PDF and after the example word analogy and series problems within these digital resources.
Example of a phase 1 word analogy
You can find more examples in Appendix 1 of your PDF, or at English For Everyone, Super Teacher Worksheets, and Education.com.
Q:Easy is to difficult as soft is to ________
A:
- a. Fragile
- b. Hard
- c. Flat
- d. Wet
Example of a phase 2 number series problem
See Appendix 1 of your PDF for more information and examples of number series.
Q:
Look at this series of numbers:
7, 42, 11, 39, __, 36, 19...
What number should fill in the blank?
A:
- a. 5
- b. 15
- c. 43
- d. 42
Example of a phase 2 letter series problem
See Appendix 1 of your PDF for more information and examples of letter series.
Q:
Look at this series of letters:
K, T, E, A, L, T, F, A, _, _, _, _
What letters come next in series?
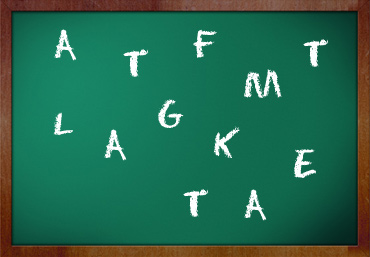
A: K, T, E, A, L, T, F, A, M, T, G, A This sequence uses the ‘NINI’ format: next in series (N), same in series (I), next in series (N), same in series (I).

Post-teaching assessment questions
Once you’ve completed the teaching assessment process, you should take time to ask yourself – and answer – these questions relating to both phases. Keep these in mind when filling in Tables 2 to 5.
- How much did the teaching assessment improve both pupils’ performance on question 1?
- How much did it improve their performance on question 3?
- How did improvements in performance on question 1 compare with those for question 3?
- What teaching approaches most helped the pupils with questions 1 and 3, and how much teaching was required?
- How does the teaching used in the assessment relate to improvements made by both pupils in both phases?
- What do the results of the assessment tell you about the pupils’ respective identifications as either MLD or lower-attaining, and how should this affect planning for their teaching?